Banks is the most popular industry in India. Be it the businessman or laborer, everyone is connected to banks in India. Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna by Narendra Modi has connected all the households of India with at least one bank account.
Banking is responsible for the maintenance of the finances of the Nation including cash and credit. These financial institutions provide services such as loans, credit cards, currency exchange, and depositing money. The banking system in India works with the public claim and social support. The main banking body of India is Reserve Bank of India (RBI), which governs the banks across the nation and responsible for regulating the monetary policy in India.
There are different types of Banks in India performing different functions. This article is enriched with the information related to the Classification of banks in India, their functions, and types.
Bank Classification in India
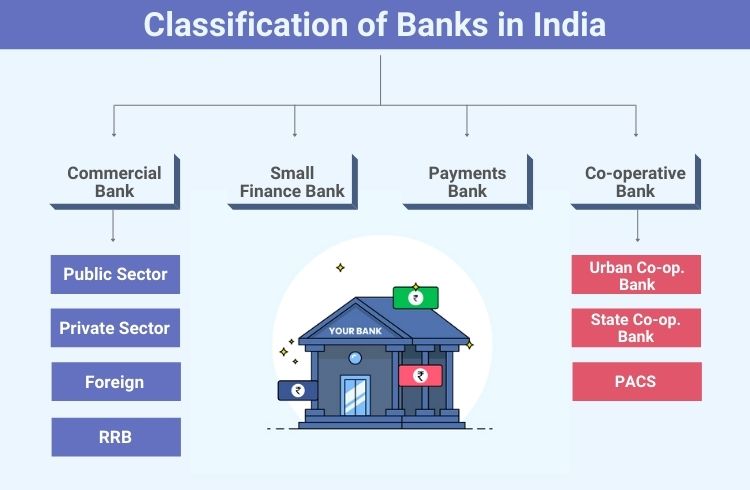
In India, various kinds of banks are working to cater to business demands, social needs, and global complexities. Various banks are giving their contribution to enable smooth functioning for the Indian financial system. That is why banks can be classified in various ways on the basis of laws and regulations, domicile, ownership, functions, and structure.
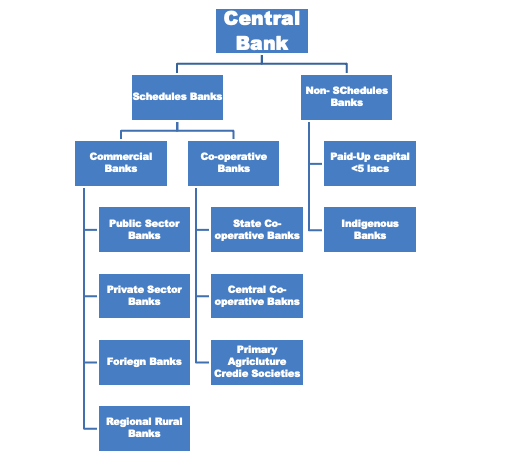
The banking system in India has classified the banks into two kinds:
- Scheduled Banks
- Non-Scheduled Banks
What is Scheduled Bank?
Scheduled Banks refer to those banks which are covered under the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. The banks that satisfy the criteria laid down by 42(6)(a) of the said act RBI includes only those banks in this category.
Banks having a paid-up capital of Rs. 5 lakhs and over are qualified for scheduled banks, and these banks can take loans from RBI at bank rate. The Scheduled Banks are further classified into two different sectors:
- Commercial Banks
- Co-operative Banks
What is Non-Scheduled Bank?
The banks which were not included in the Second Schedule of Reserve Bank of India Act,1934 are non-scheduled banks, and these do not follow all the banking rules laid by RBI. To qualify as a non-scheduled bank:
- It should be corporation, instead of sole-proprietorship or partnership firm.
- Should have a paid capital of >INR 5 lacs.
- Should satisfy RBI that it won’t causes harm to the interest of the depositors.
Types of Banks in India

In India, there are many ways, through which banking may be done. To facilitate this, there are different types of banks on the market in India.
Below is the list of types of banks in India:
- Central Banks
- Commercial Banks
- Co-Operative Banks
- Local Area Banks (LAB)
- Specialized Banks
- Small Finance Banks
- Payment Banks
Let us discuss these banks one by one.
1. Central Bank
RBI is the central bank in India that governs and regulates the other banks working throughout the country. Central Bank guides the other banks, issue currency, implement the monetary policies and supervise the financial system. It is also called the banker’s bank.
2. Commercial Bank
Commercial banks were regulated under the Banking Regulation Act,1949 to operate on a commercial basis and earn a profit. These banks have a unified structure and can be run by any government or private entity and tend to all sectors whether rural or urban.
Types of Commercial Bank
- Public Sector Banks
- Private Sector Banks
- Foreign Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRB)
Public Sector Banks
In public sector banks, Government or the RBI are the major stake owners. These banks are nationalized and a large part of the Indian banking system revolved around this sector. These nationalized banks cover about 75 percent of the total banking business in India. Indian government holds the majority of its stakes in these banks. The largest bank in the public sector is SBI (State Bank of India). India has now 12 nationalized banks.
List of Public Sector Banks
| S.No. | Name of Bank | Establishment | Address |
| 1 | Bank of Baroda | 1908 | Central Office, P.O. Box No. 10046, 9th Floor, Baroda Corporate Centre, Bandra Kurla Complex, Bandra (East), Mumbai – 400051 |
| 2 | Bank of India | 1906 | Head Office, Star House, C-5, G-Block, Bandra Kurla Complex, Bandra (East), Mumbai – 400051 |
| 3 | Bank of Maharashtra | 1935 | Head Office, Lokmangal, 1501, Shivaji Nagar, Pune – 411005 |
| 4 | Canara Bank | 1906 | Head Office, 112, J.C. Road, P.B. No. 6648, Bangalore – 560002 |
| 5 | Central Bank of India | 1911 | Head Office, Chandramukhi, Nariman Point, Mumbai – 400021 |
| 6 | Indian Bank | 1907 | Head Office, 31, Rajaji Road, Chennai – 600001 |
| 7 | Indian Overseas Bank | 1937 | Central Office, 763, Anna Salai, P.B. No. 3765, Chennai – 600002 |
| 8 | Punjab National Bank | 1894 | Head Office, 7, Bhikaji Cama Place, Africa Avenue, New Delhi – 110066 |
| 9 | Punjab & Sind Bank | 1908 | Head Office, Bank House, 21, Rajendra Place, New Delhi – 110008 |
| 10 | Union Bank of India | 1919 | Head Office, 239, Vidhan Bhavan Marg, Nariman Point, Mumbai – 400021 |
| 11 | UCO Bank | 1943 | Head Office, 10, B.T.M. Sarani, Brabourne Road, Calcutta – 700001 |
| 12 | State Bank of India | 1955 | Central Office, State Bank Bhavan, Madam Cama Road, Mumbai – 400021 |
Private Sector Bank
In these banks, private organization or the group of people owns the stakes. These banks also have to follow the rules and regulations set by RBI.
List of Private Sector Banks
| S.No. | Name of Bank | Establishment | Address |
| 1 | Axis Bank | 1993 | Axis Bank Limited, ‘Trishul’, 3rd Floor, Opp. Samartheshwar Temple, Near Law Garden, Ellisbridge, Ahmedabad, Gujarat – 380006 |
| 2 | Bandhan Bank of Bandhan Financial Services | 2015 | BN 5, BN Block, Sector V, Bidhannagar, Kolkata, West Bengal – 700091 |
| 3 | Catholic Syrian Bank | 1920 | Head Office, CSB Bhavan, P.O Box No. 502, St. Mary’s College Road, Thrissur, Kerala – 680020 |
| 4 | City Union Bank | 1904 | “Narayana” No. 24B, Gandhi Nagar, Kumbakonam, Tamil Nadu – 612001 |
| 5 | Dhanlaxmi Bank | 1927 | Dhanalakshmi Buildings Naickanal, Thrissur, Kerala – 680001 |
| 6 | Development Credit Bank | 1930 | P.O. Box No. 7643, Malad (West), Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400064 |
| 7 | Federal Bank | 1931 | Federal Towers, PB No. 103, Aluva, Ernakulam, Kerala – 683101 |
| 8 | HDFC Bank | 1994 | HDFC Bank House, Senapati Bapat Marg, Lower Parel, Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400013 |
| 9 | IDFC Bank | 2015 | 4th Floor, Capitale Tower, 555 Anna Salai, Thiru Vi Ka Kudiyiruppu, Teynampet Chennai, Tamil Nadu – 600018 |
| 10 | IDBI Bank | 1964 | IDBI Tower, WTC Complex, Cuffe Parade, Colaba, Mumbai – 400005 |
| 11 | ICICI Bank | 1994 | ICICI Bank Tower, Near Chakli Circle, Old Padra Road, Vadodara, Gujarat – 390007 |
| 12 | Induslnd Bank | 1994 | IndusInd Bank Limited, 2401 Gen. Thimmayya Road (Cantonment), Pune, Maharashtra – 411001 |
| 13 | Jammu and Kashmir Bank | 1938 | M A Road, Srinagar, Jammu & Kashmir – 190001 |
| 14 | Karnataka Bank | 1924 | Post Box No. 599.Mahaveera Circle, Kankanady, Dakshina Kannada Dist., Mangaluru, Karnataka – 575002 |
| 15 | Karur Vysya Bank | 1916 | No. 20, Erode Road, Vadivel Nagar, L.N.S., Karur – 639002 |
| 16 | Kotak Mahindra Bank | 2003 | 27 BKC, C-27, G-Block, Bandra Kurla Complex, Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400051 |
| 17 | Laxmi Vilas Bank | 1926 | Baba Kharak Singh Marg, Connaught Place, New Delhi – 110001 |
| 18 | Nainital Bank | 1922 | GB Pant Road, Malli Tal, Nainital – 263001 |
| 19 | Ratnakar Bank | 1943 | 1st Lane, Shahupuri, Kolhapur, Maharashtra – 416001 |
| 20 | South Indian Bank | 1929 | T.B Road, Mission Quarters, Thrissur, Kerala – 680001 |
| 21 | TamilNad Mercantile Bank | 1921 | 57, V.E. Road, Tuticorin, Tamil Nadu – 628002 |
| 22 | Yes Bank | 2004 | ONE International Center, Tower II, 15th Floor, Senapati Bapat Marg, Elphinstone (W), Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400013 |
Foreign Sector Banks
Some of the foreign banks have branches In India and headquarters abroad. These types of banks are included in this sector. These banks follow the rules and regulations of their country’s central bank as well as RBI. The number of foreign banks in India is more than 40.
List of Foreign Sector Banks
| S.No. | Name of Bank | Establishment | Address |
| 1 | Australia and New Zealand Banking Group Ltd (ANZ) | 1951 | Melbourne, Australia |
| 2 | National Australian Bank (NAB) | 1981 | Melbourne, Australia |
| 3 | Royal Bank of Scotland (RBS) | 1727 | Edinburgh, United Kingdom |
| 4 | Barclays Bank | 1896 | London, United Kingdom |
| 5 | Bank of America | 1998 | Charlotte, North Carolina, United States |
| 6 | Doha Bank | 1979 | Doha, Qatar |
| 7 | Westpac Banking Corporation | 1982 | Sydney, Australia |
| 8 | The Bank of Bahrain & Kuwait (BBK) | 1971 | Manama, Bahrain |
| 9 | AB Bank Ltd | 1982 | Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| 10 | HongKong and Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC) | 1865 | London, United Kingdom |
| 11 | CITI Bank | 1812 | New York, United State of America (USA) |
| 12 | Deutsche Bank | 1870 | Frankfurt, Germany |
| 13 | Development Bank of Singapore (DBS Bank Ltd) | 1968 | Marina Bay, Singapore |
| 14 | United Overseas Bank Ltd (UOB) | 1935 | Singapore |
| 15 | J P Morgan Bank | 2000 | New York, United State of America (USA) |
| 16 | Standard Chartered Bank (SCB) | 1969 | London, United Kingdom |
Regional Rural Banks (RRB)
These banks work for the agriculture and rural sectors. These Banks were established in 1975 and registered under Regional Rural Bank Act, 1976. The stakes of these banks are owned by the Central bank (50%), State Government (15%), and Commercial Bank (35%).
List of RRBs in India
| S.No. | State | Name of the RRB |
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh | Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank Saptagiri Grameena Bank |
| 2 | Arunachal Pradesh | Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank |
| 3 | Assam | Assam Gramin Vikash Bank Langpi Dehangi Rural Bank |
| 4 | Bihar | Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank Bihar Gramin Bank Madhya Bihar Gramin Bank |
| 5 | Chhattisgarh | Chhattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank |
| 6 | Gujarat | Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank Saurashtra Gramin bank Dena Gujarat Gramin Bank |
| 7 | Haryana | Sarva Haryana Gramin Bank |
| 8 | Himachal Pradesh | Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank |
| 9 | Jammu & Kashmir | Ellaquai Dehati Bank J&K Grameen Bank |
| 10 | Jharkhand | Vananchal Gramin Bank Jharkhand Gramin Bank |
| 11 | Karnataka | Pragathi Krishna Gramin Bank Kaveri Gramin Bank Karnataka Vikas Gramin Bank |
| 12 | Kerala | Kerala Gramin Bank |
| 13 | Madhya Pradesh | Narmada Jhabua Gramin Bank Central Madhya Pradesh Gramin Bank Madhyanchal Gramin Bank |
| 14 | Maharashtra | Vidharbha Konkan Gramin Bank Maharashtra Gramin Bank |
| 15 | Manipur | Manipur Rural Bank |
| 16 | Meghalaya | Meghalaya Rural Bank |
| 17 | Mizoram | Mizoram Rural Bank |
| 18 | Nagaland | Nagaland Rural Bank |
| 19 | Odisha | Odisha Gramya Bank Utkal Grameen Bank |
| 20 | Puducherry | Puduvai Bharathiar Grama Bank |
| 21 | Punjab | Punjab Gramin Bank Malwa Gramin Bank Sutlej Gramin Bank |
| 22 | Rajasthan | Baroda Rajasthan Kshetriya Gramin Bank Rajasthan Marudhara Gramin Bank |
| 23 | Tamil Nadu | Pallavan Grama Bank Pandyan Grama Bank |
| 24 | Telangana | Telangana Grameena Bank |
| 25 | Tripura | Tripura Gramin Bank |
| 26 | Uttar Pradesh | Gramin Bank or Aryavart Allahabad UP Gramin Bank Baroda Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank Kashi Gomti Samyut Gramin Bank Sarva UP Gramin Bank Prathama UP Gramin Bank Purvanchal Bank |
| 27 | Uttarakhand | Uttarakhand Gramin Bank |
| 28 | West Bengal | Bangiya Gramin Vikash Bank Paschim Banga Gramin Bank Uttarbanga Kshetriya Gramin Bank |
3. Co-operative Banks
All those banks which run by an elected managing committee working on no-gain no-loss and are registered under the Co-operative Societies Act 1912, are known as Co-operative banks.
These banks finance agricultural activities like farming, hatcheries, etc. in rural areas and small businesses, self-employment, and industries in non-rural areas.
These banks are divided into three types. Those are:
A. Urban Co-operative Banks
The banks located in semi-urban and urban, which finance small businesses.
B. State Co-operative Banks
The bank is an association of central co-operative bank and acts as a protector of the collaborative banking system in the state. Its funds are gained from the overdrafts, social capital, loans, etc.
C. Primary Agricultural Credit Society (PACS)
A Primary Agricultural Credit Society (PACS) is a basic unit and smallest co-operative credit institutions, which works on the grassroots level (gram panchayat and village level).
4. Local Area Banks (LAB)
These banks were introduced in India in 1996 and registered under the Companies Act 1956. These are organized by the private sector and there are only 4 local area banks in India (South India).
List of Local Area Banks
- Coastal Local Area Bank Ltd.
- Capital Local Area Bank Ltd.
- Krishna Bhima Samruddhi Local Area Bank Ltd.
- Subhadra Local Area Bank Ltd.
5. Specialized Banks
These banks are established for a specific purpose only. These are:
- Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI)- These banks are set up to provide loan facilities to small-scale industries and businesses. This bank is also responsible for providing modern technology equipment to small-scale industries.
- EXIM Bank (Export And Import Bank)- EXIM bank is responsible for providing loans or any financial assistance with the export or import of the goods.
- National Bank of Agricultural and Rural Development (NBARD) – This bank is responsible for providing financial assistance to the rural, Handicraft, village, and Agricultural development.
6. Small Finance Banks
These banks provide loans and financial support to the small farmers, Micro industries, and other unorganized sectors of society. RBI Governs these Banks also.
List of Small Finance Banks
- AU Small Finance Bank
- Capital Small Finance Bank
- Esaf Small Finance Bank
- Equitas Small Finance Bank
- Fincare Small Finance Bank
- Utkarsh Small Finance Bank
- Jana Small Finance Bank
- Suryoday Small Finance Bank
- Northeast Small Finance Bank
- Ujjivan Small Finance Bank
7. Payments Banks
The payment banks are conceptualized by the RBI but customers of these banks cannot avail loans or credit cards and the deposit limit is Rs. 1 lacs only. Customers can get the facilities like online banking, ATMs, Debit cards, etc.
List of Payment Banks
- Airtel Payments Bank
- India Post Payments Bank
- Jio Payments Banks
- Paytm Payments Bank
- NSDL Payments Bank
Functions of Bank
The bank is the organization that accepts deposits from the public which can be withdrawn when needed. This enables people to manage their finances in their bank accounts. Banks give two assurances to the public- Safe deposit and on-demand withdrawal. The additional interest on the deposited amount gives extra benefits to the account holders. Along with the saving facility, Banks also grant loans to the public.
1. Primary Functions of Banks
- Accepting Deposits
- Granting Loans
Accepting Deposits
Accepting deposits from the public is the basic function of banks in India. This helps people to develop a habit of saving money. There are different kinds of money depositing accounts for different purposes.
- Saving Accounts – This is the best deposit for salary earners as it has no limit on the number of withdrawals. The account holder also gets a small amount of interest on the deposit. This can be opened in the name of a single account holder or a joint account. Banks provide ATM cum debit card, cheque book, and internet banking services to the saving account holders. There is a minimum limit that the account holder has to maintain in the deposit.
- Fixed Deposit – Fixed Deposit or Term Deposit enables people to deposit money for a fixed tenure and no can be withdrawn during this period. In case, if a depositor withdraws money before the completion of tenure, the bank puts a penalty. If depositors complete the tenure, banks will provide them the promised amount. The rate of interest is very high in this kind of deposit and varies according to the period.
- Current Deposit – These bank accounts are the best for Business purposes. The account holders get the overdraft facility and these deposits work like short-term loans for fulfilling urgent needs. The high-interest rates are charged by the banks along with overdraft charges in order to maintain the reserve for unknown demands for overdraft.
- Recurring Deposit – The account holders are required to deposit a fixed amount of money at regular intervals and money can be withdrawn after the completion of tenure. The rate of interest is very high in this deposit as the account holders get the compound interest. A big amount of money is provided at the end. Small merchants and salaried persons use this.
Granting Loans
Bank uses the public’s money for lending loans to the businessmen or people to meet their emergencies. The bank charges a very high rate of interest on loans. The banks get profit from the difference between the rate of interest for deposits and the rate of interest on loans.
Following types of loans are granted by the Banks:
- Bank Overdraft: These loans are provided to the businessmen. They can withdrawal more money than the amount in their accounts and have to deposit it back before a certain limit. The rate of interest is charged on the amount borrowed.
- Cash Credits: Banks grant these loans to all types of account holders and even to those also who don’t have an account with the bank. These loans are granted against a mortgage of any property in the name of the borrower. Cash credits are short-term loans with a very high rate of interest is charged on the money withdrawn.
- Loans: Banks lend these loans for a longer period like 1 to 5 years or more against any tangible asset. The borrower has to pay installments on a regular basis as decided by the bank during lending the loan. The rate of interest is charged on the total amount whether withdrawn or not.
- Discounting the bills of Exchange: In these short-term loans, sellers discount the bill from the bank for certain fees. Banks advance money by discounting the bills of exchange. The bill is directly paid to the seller on behalf of the buyer and discount charges are deducted. At the end of the fixed tenure, the bank presents the bill to the seller or buyer to collect the amount.
2. Secondary Functions of Banks
- Agency Functions
- Utility Functions
Agency Functions of Banks
Banks also work as agents for their customers. Let’s have at the Agency functions of banks are:
- Transfer of Funds- Banks help their customers to transfer money from one bank to another.
- Periodic Payments- Banks also pay the electricity bills, water bills, etc. on behalf of the customer. These are called periodic payments.
- Periodic Collections- Banks collect periodic payments on behalf of the customer. These include salaries, Pensions, etc.
- Cheque collections- The banks collect the cheque’s money through the clearing section of the customers same as collecting money from the bill of exchange.
- Portfolio Management- The banks manage the activities of their customers regarding sales and purchase of shares and debentures, etc.
- Other Agency functions- The banks are the executors, trustees, advisors, etc. for their customers.
Utility Functions of Banks
- Issuing letters of credits, traveler’s cheques, etc.
- Locker facilities for important documents, valuable assets, etc.
- Foreign exchange dealing
- Shares and debentures underwriting
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. I want to start a small business and have a saving account in SBI. Can I apply for a loan?
Ans. Yes, you can apply for a Loan in SBI for your business. You can ask about the rules and regulations of the loan from any SBI branch near you.
Q2. What is the difference between Fixed Deposit and Recurrent Deposit?
Ans. Fixed Deposit is where you deposit an amount to the bank for a certain period, say, Rs. 50,000 for 1 year and you will get the amount along with the promised interest at the end of the tenure. A recurrent Deposit is when you have to deposit a particular amount at a regular interval of time for a certain period, say, Rs.5000 per month for 1 year and you get the total amount along with interest at the end.
Q3. Which deposit is good? FD or RD?
Ans. It depends on your financial conditions. If you are comfortable with depositing every month, you can go for RD, and if you have a big amount and you want to fix it for some time, go for FD.
Q4. Is a savings account good for business purposes?
Ans. No, Saving Account is not for business purposes. It is for regular saving purposes and better for salaried people. For business purposes, you can go for the Current Account.
Q5. What is the minimum limit for maintaining a Current Account?
Ans. The minimum balance limit varies from bank to bank. You can go to the bank and ask personally.
Q5. How many public sector banks in India?
Ans. There are 12 public sector (Nationalised) banks in India now. They are Bank of Baroda, Bank of India, Bank of Maharashtra, Canara Bank, Central Bank of India, Indian Bank, Indian Overseas Bank, UCO Bank, Union Bank of India, Punjab & Sind Bank, Punjab National Bank, and State Bank of India.



